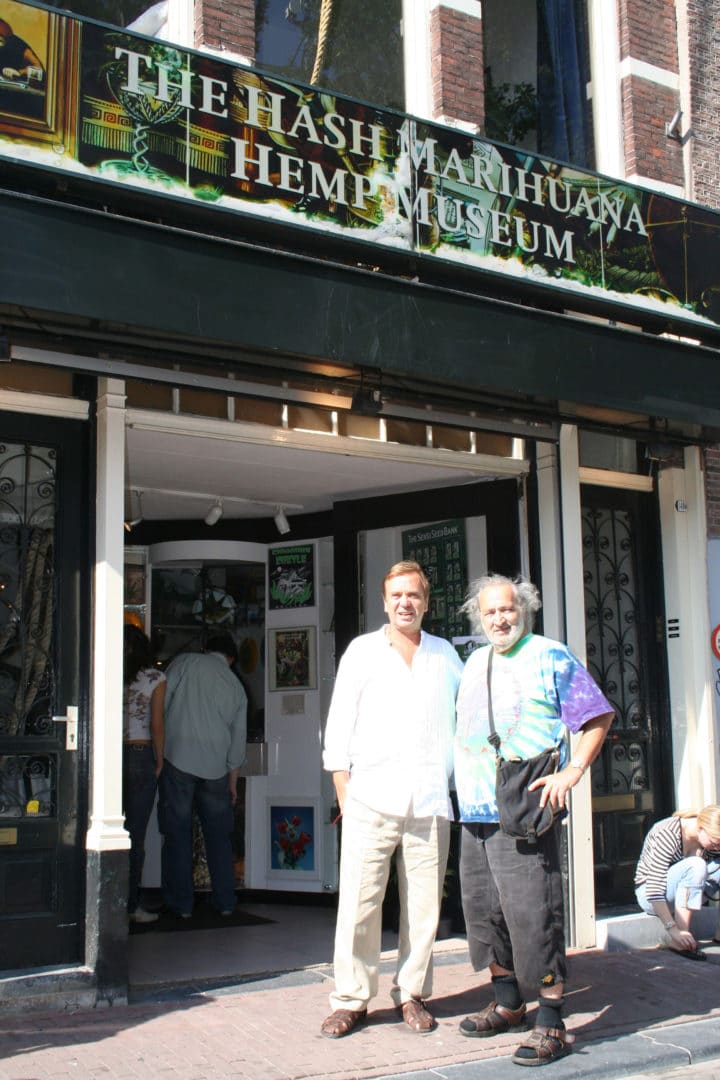
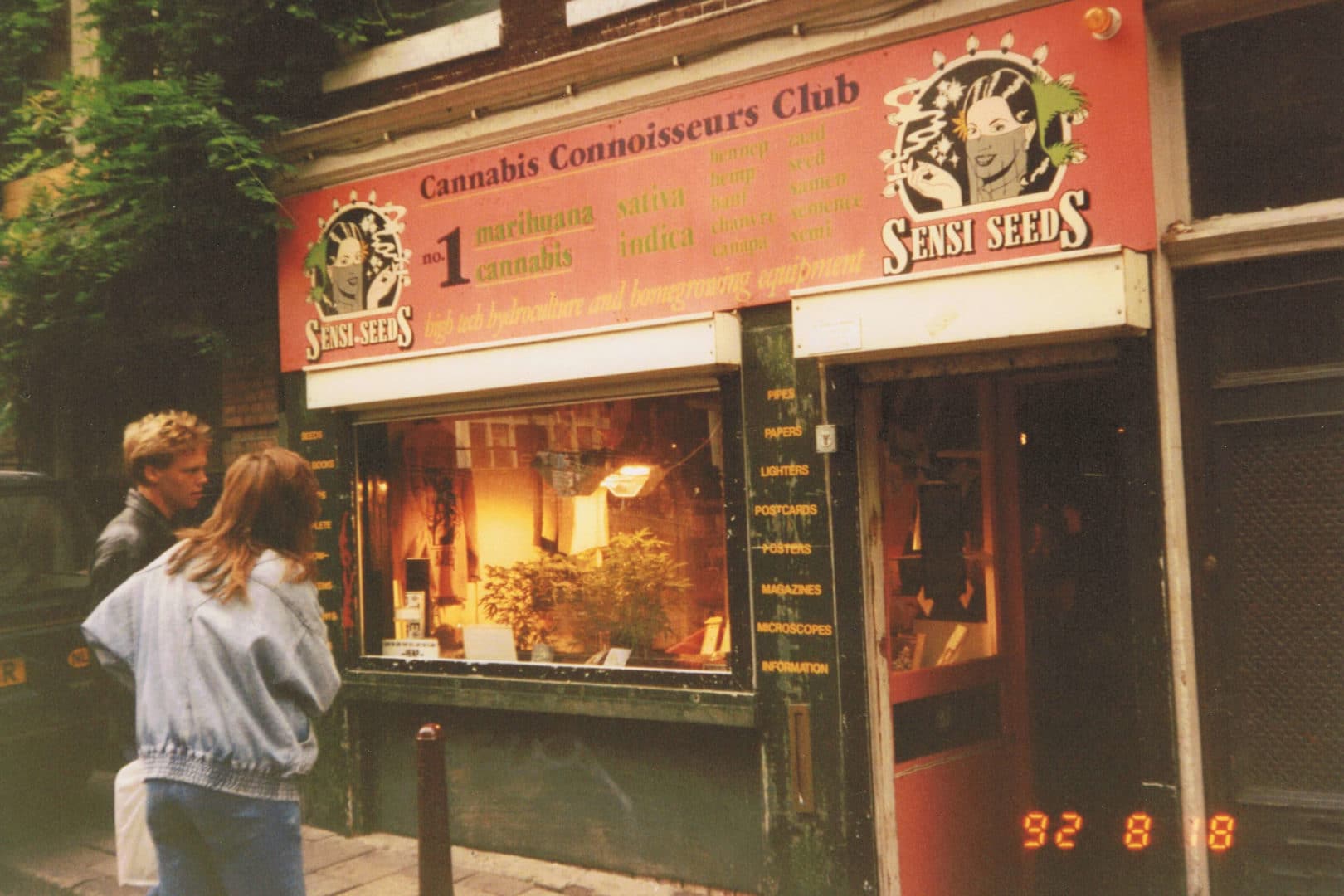
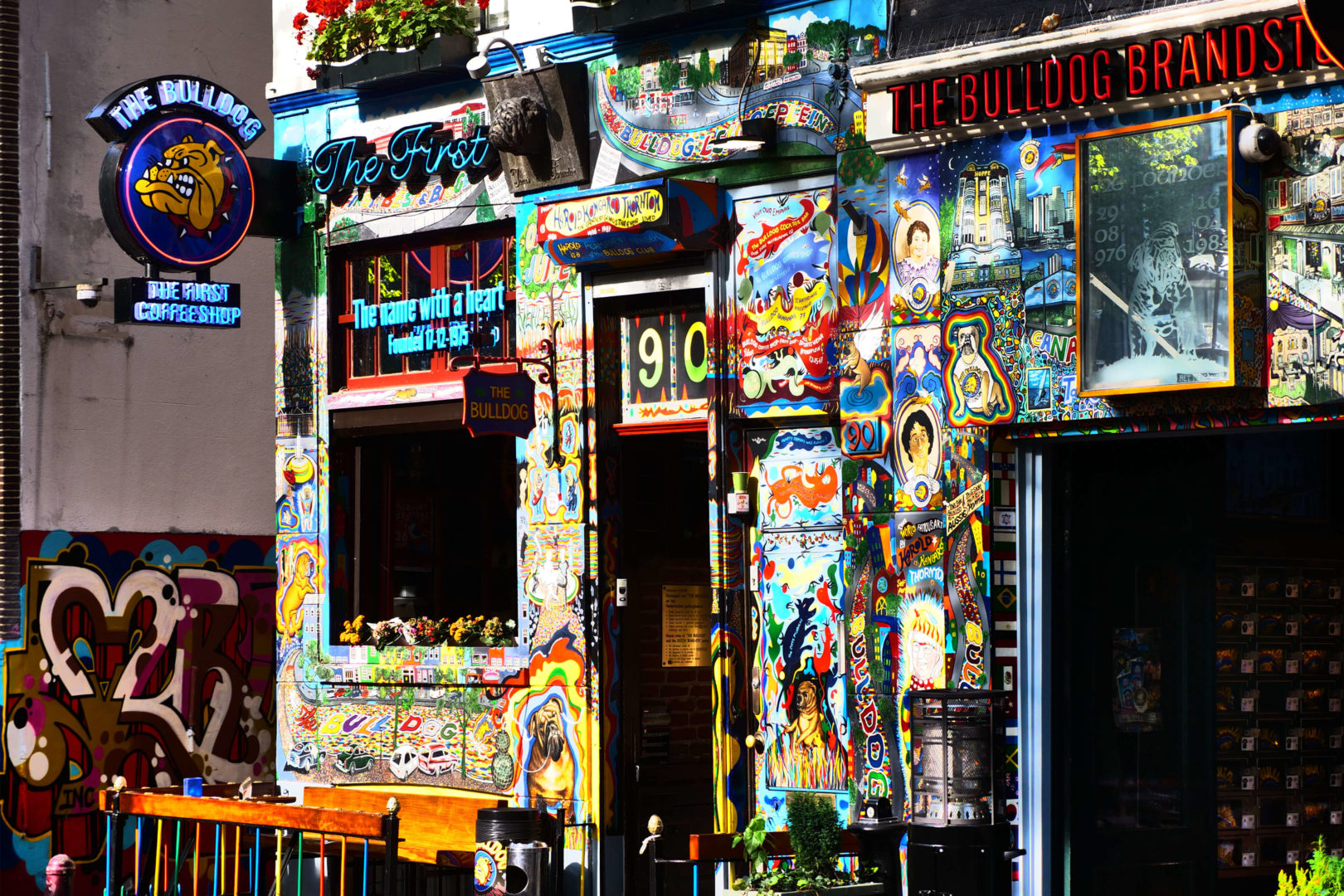
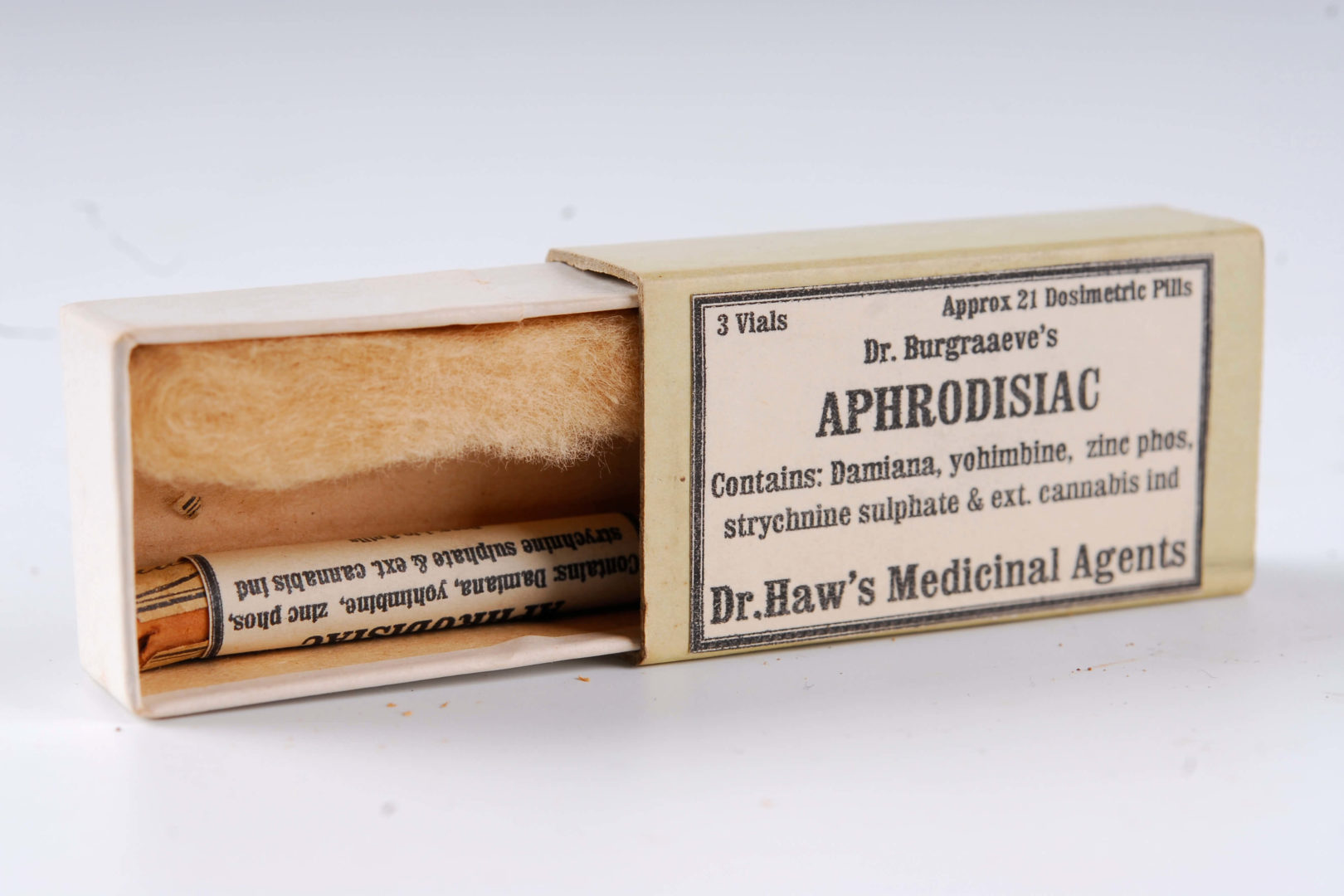
11. Hortus Botanicus
In the 17th century, medicinal herbs were vital to Amsterdam’s health care. Therefore, when the Hortus was founded in 1638, it was logical that medicinal plants made up the core of the plant collection. This was known as the Hortus Medicus. The Hortus today features a unique garden of medicinal plants which were grown there […]